Simba
Simplify Access to Data Across Applications and Data Platforms
Simba Data Connectors provide trusted access to data anywhere, relentlessly optimized for performance and functionality.
"*" indicates required fields
Do You Need To Simplify How You Currently Connect, Integrate And Access Data?
Wasting Time and Budget
Software vendors, are you spending unnecessary time and budget sourcing, maintaining, and managing ad-hoc data drivers or using APIs to deliver data access?
Problems Connecting Data to BI Tools
No more exporting, no more outdated enterprise data – just easy access to the right data, in real time, regardless of where it resides.
Does Data Access Quality Put Your Application at Risk?
You can’t afford to treat high-quality, broad-based connectivity to data as an afterthought, but building it may be a distraction you can’t afford.
Trusted By
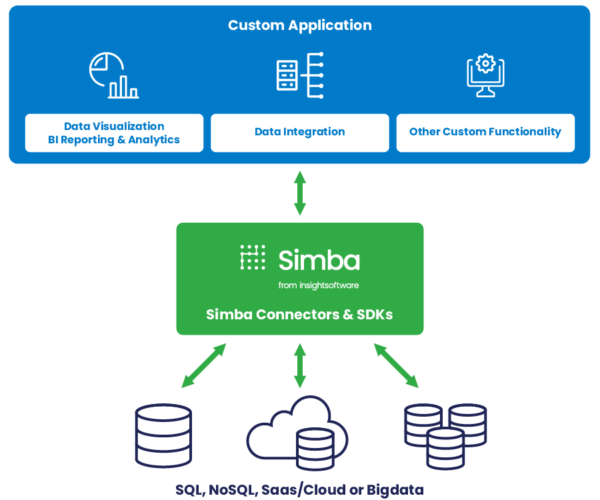
Connectivity for Software Vendors
Drive faster time to market while extending the possibilities of your BI solution, custom application, database or data platform by enabling connectivity to your customers’ data sources of choice. Do it all with connectivity solutions and services from the creators of ODBC, whose technology is embedded into leading operating systems and data platforms.
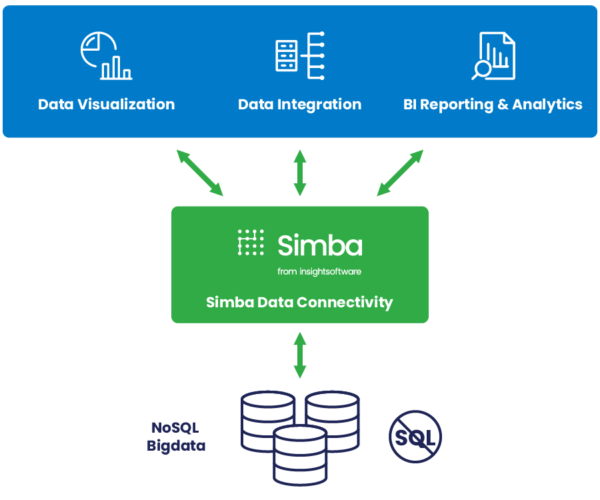
Connectivity for the Enterprise
Empower your business users with trusted data by connecting reliably to multiple data sources in real time. Keep your data safe, enable real-time federation and migrate to the cloud or deliver integration for your transformation initiatives – without disruption. Experience the power of a connectivity platform with more than one billion deployments around the world.
Simba Data Connectors
Quick & comprehensive access to business intelligence
Connect any data source to your business intelligence tool or application of choice.
Easily access data and link with legacy and next-generation tools and applications. Companies worldwide partner with Simba to enable seamless connections.
We build drivers to current standards with reliability, scale, and security … so you don’t have to.

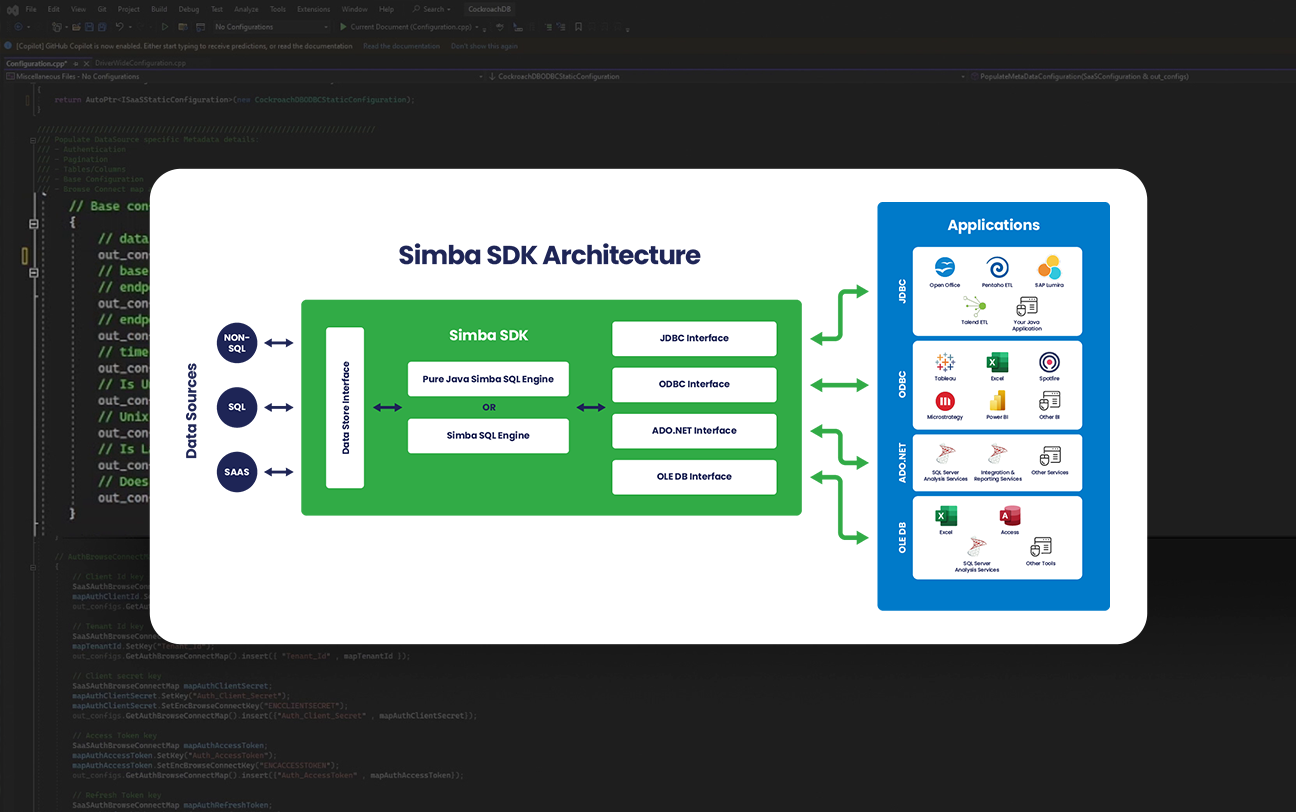
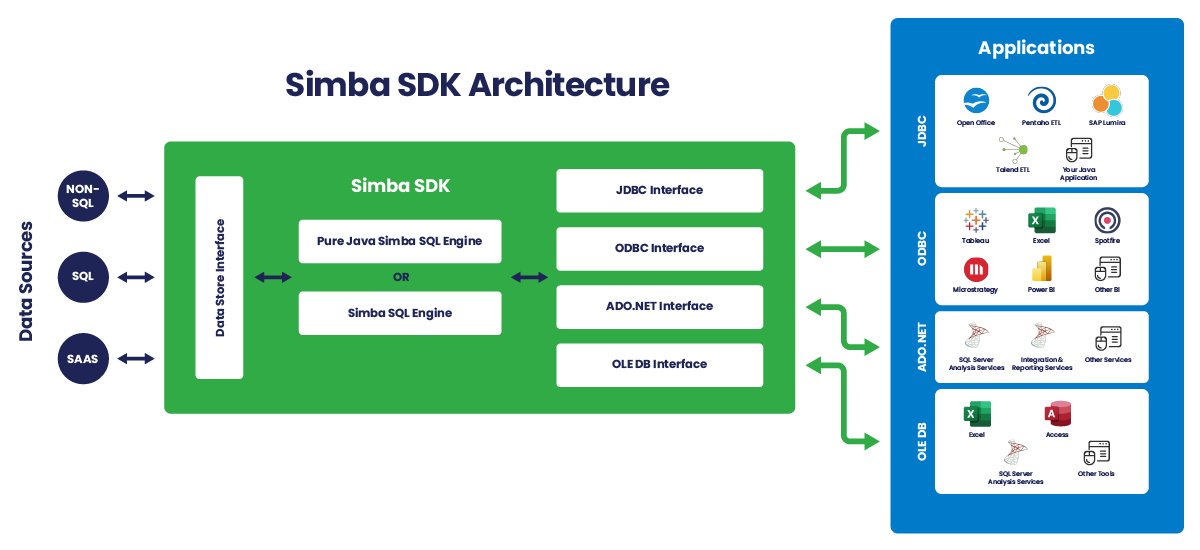
Simba SDK
Develop your own custom driver
The same Simba Software Development Kit (SDK) that our engineering team uses to develop Simba drivers is available for you to develop your custom ODBC/JDBC driver for any SQL-enabled or NoSQL data source. Because sometimes DIY just makes sense.
Reduce cost, complexity, risks, and time-to-market compared to developing a driver from scratch.
Benefits to using the Simba SDK for ODBC/JDBC driver development:
- Speed Up Development: Develop a driver proof-of-concept in as few as five days.
- Be Flexible: Deploy your driver as a client-side, client/server, or cloud solution.
- Extend Your Data Source Reach: Connect your applications to any data source, be it SQL, NoSQL, or proprietary.
- Rely on Proven Technology: Partners like Cloudera, Microsoft, Teradata, SAP, and MapR embed Simba SDK-developed drivers in their own products.
Simba Managed Services
Drivers are a vital feature of data-driven applications. However, building, testing, and maintaining those drivers are often outside a team’s core competencies.
How will you connect to relational and NoSQL databases, Big Data sources such as Hadoop, and SaaS and cloud sources like Salesforce, Google BigQuery, or Amazon Athena? How will you keep these connections updated or add new ones as you grow?
Engage with our Simba Managed Services for a flexible, high-touch approach that offloads the burden and abstracts away the complexity of data connectivity.
- SDK-Licensed Development & Testing Managed Services: Let Magnitude do all the development or augment your team
- Driver Customization Managed Services: Easily extend driver capabilities to support advanced enterprise services and platforms
- Engineering Services: We’ll develop your IP or open-source code — without license costs, fully integrated into your internal processes

Need a Data Connector – See Our Portfolio
The Data Connectivity Leader
100% of Gartner BI Magic Quadrant Leaders use Simba Data Connectivity solutions > 1 Billion total deployments

Magnitude Simba was a natural choice as the drivers are trusted by the data source vendors and guaranteed to be compatible with any data source. Business users can connect their Sisense BI tool seamlessly to their disparate data, enabling them to analyze billions of rows and extract insights from these data sets with unparalleled speed and smooth performance without having to write code.
Speak to an Expert








